Anal Cancer


What is anal cancer?
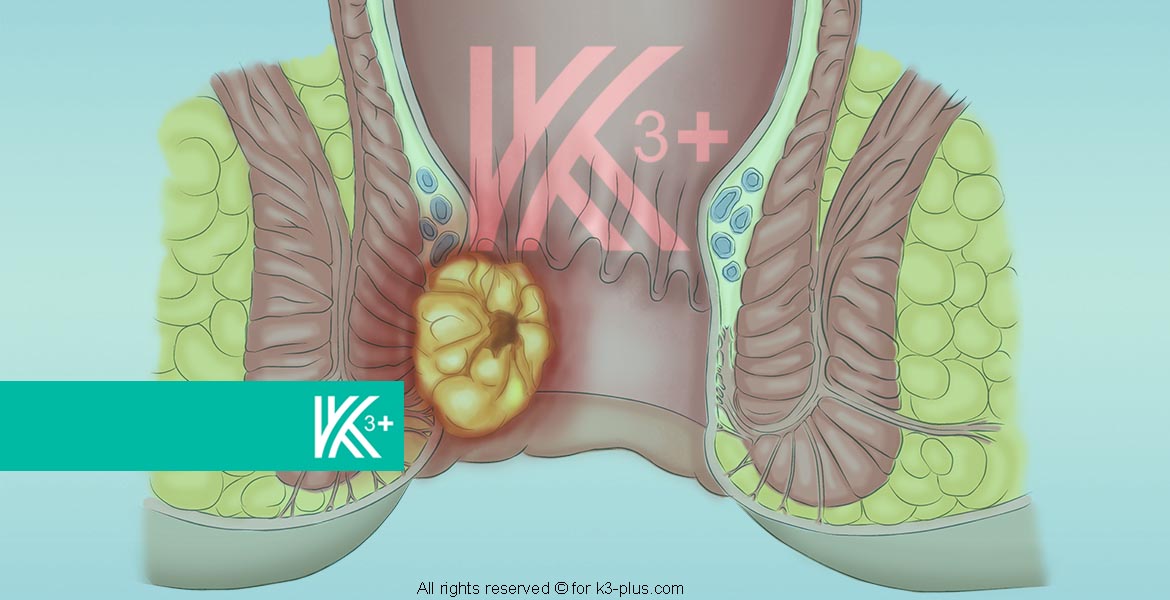
It is an uncommon cancer in which malignant cancer cells are concentrated and collect in the anal area at the anal opening where stool is expelled from the body. This cancer most often appears outside the anus in men, and it is usually internal in women.
The main symptom of anal cancer is that the anus is swollen and sore. The tumors that may appear in the perianal skin region have nothing to do with that, as they are often different skin tumors and not anal cancer.
Anal cancer diagnosis
- Rectal bleeding, even if in small amounts
- Rectal pressure
- Pain in the anal area
- Anal itching
- Discomfort at the anus,
- A lump at the anus.
In the doctor’s office, and if there are symptoms of cancer, the doctor examines the inner and outer parts of the anus, the outer part by direct examination, and the inner part, the doctor wears thin gloves and then applies an oily substance to his finger and inserts it into the rectum to gently feel for any tumors or bumps.
The doctor also checks every substance attached to the gloves to make sure they contain blood. If the patient feels pain, and to complete the examination, the doctor suggests completing the examination with complete anesthesia or administering a sleeping drug, depending on the patient’s situation and decision. It also takes a biopsy of the tissue to be examined under the microscope and to make sure that there are no cancer cells even if they are not visible or perceptible.
One of the factors that increase the risk of anal cancer is infection with the human papillomavirus, as well as in homosexuals. Anal cancer remains uncommon, as it constitutes only 4% of cancers of the lower digestive system, and chemotherapy and radiotherapy have proven highly effective in treating it.
The chance of cure from this disease and the method of treatment depend on the stage the cancer has reached (whether it is in the anus only or if it has spread to other parts of the body) as well as on the general health of the patient.
Three important factors in achieving a cure for anal cancer are:
- Location
- the size
- Differentiation ratio or differentiation Well-differentiated tumors are more benign than poorly differentiated tumors.
Epidermoid tumor
It is a desquamated cell carcinoma and represents most of the cases that affect the anus, while the remaining cancers are formed from the important subgroup of transitional cells. These tissue changes accompany HPV infection.
“Currently, Dr. Khaldoun Ghareb is proud to provide early diagnosis and treatment of anal cancer with the latest international methods”
Anal Cancer FAQs
I have a lump near the anus, how do I know if it is cancer so I can treat it or is it just a harmless hemorrhoid?
I feel a swelling or a lump in the anus, and I do not know the reason for that. This sensation began a year ago and is still present. Do I have to see a doctor?
The doctor told me that I have a cancerous tumor in the anus, and he advised me for chemotherapy. Any advice?
I read about anal cancer and wanted to know if there was some way to avoid it, such as a certain diet?
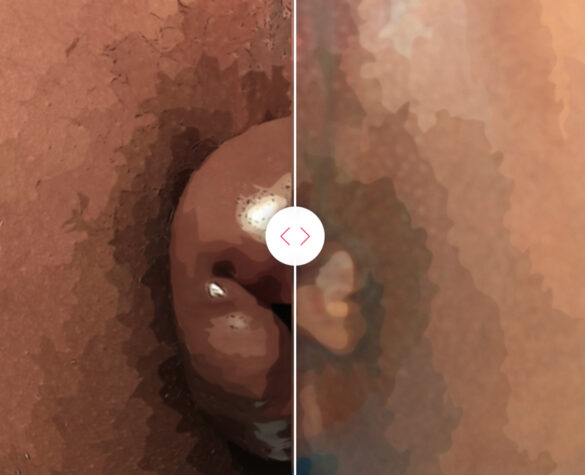
Anal Cancer Cases
Patients who previously lived suffering from hemorrhoids, fistulas, and hair bags, and received treatment by Dr. Khaldoun. We list the symptoms they suffered and the treatment that was provided, which could be useful for you.