Faecal Incontinence
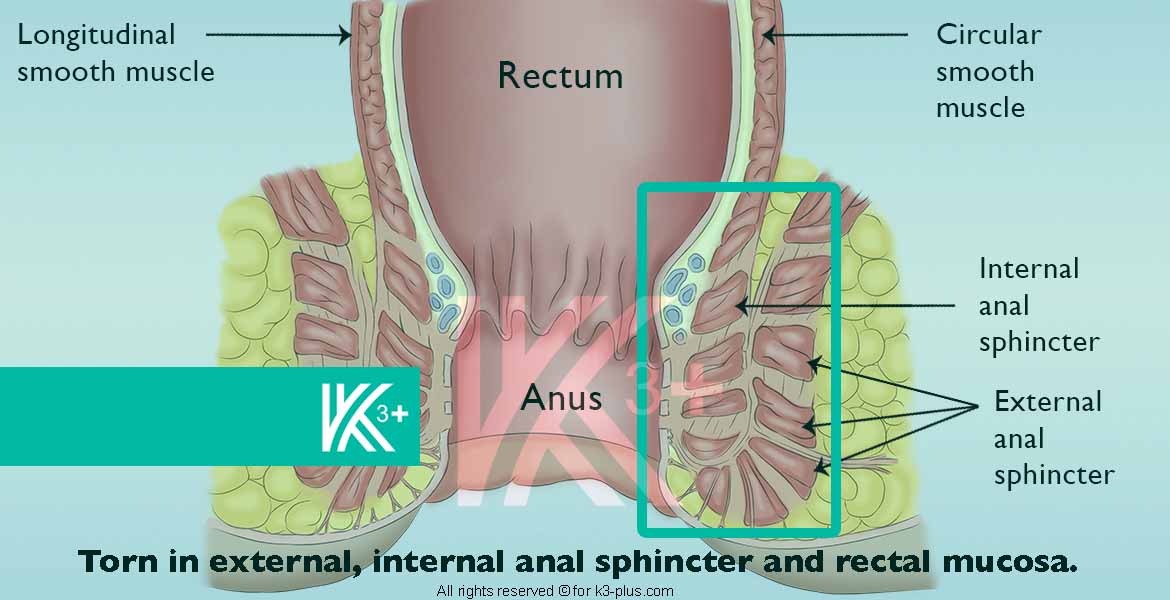



What is fecal incontinence?
Faecal incontinence is the inability to control the initiation or stopping of a bowel movement, which causes stool to leak unexpectedly from the rectum. Fecal incontinence, also known as bowel incontinence, ranges from accidental leakage of stools while passing gases to a complete loss of bowel control.
Causes of faecal incontinence
The cause of faecal incontinence is constipation, diarrhea, and muscle or nerve damage, which may be the result of aging or childbirth. It is an embarrassing disease sometimes. But don’t be shy to talk to your doctor. He can use fecal incontinence treatments that may change your life.
In the following video, Dr. Khaldoun Ghareb explains about faecal incontinence and the treatment used
Symptoms of faecal incontinence
Temporary fecal incontinence ; Incontinence is the result of an occasional event such as severe diarrhea and it does not always recur
Fecal incontinence Alalhahi ; It is the chronic incontinence of faeces and the inability to stop defecation, so the person suddenly breaks and does not allow him time to go to the bathroom.
Negative faecal incontinence; It is faecal incontinence that occurs as a result of the unaware of the stool leaving the anus.
Symptoms accompany fecal incontinence
Problems that may accompany fecal incontinence are often found in the intestine, such as:
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Gas and bloating
Causes of faecal incontinence
Things that increase the risk of fecal incontinence are:
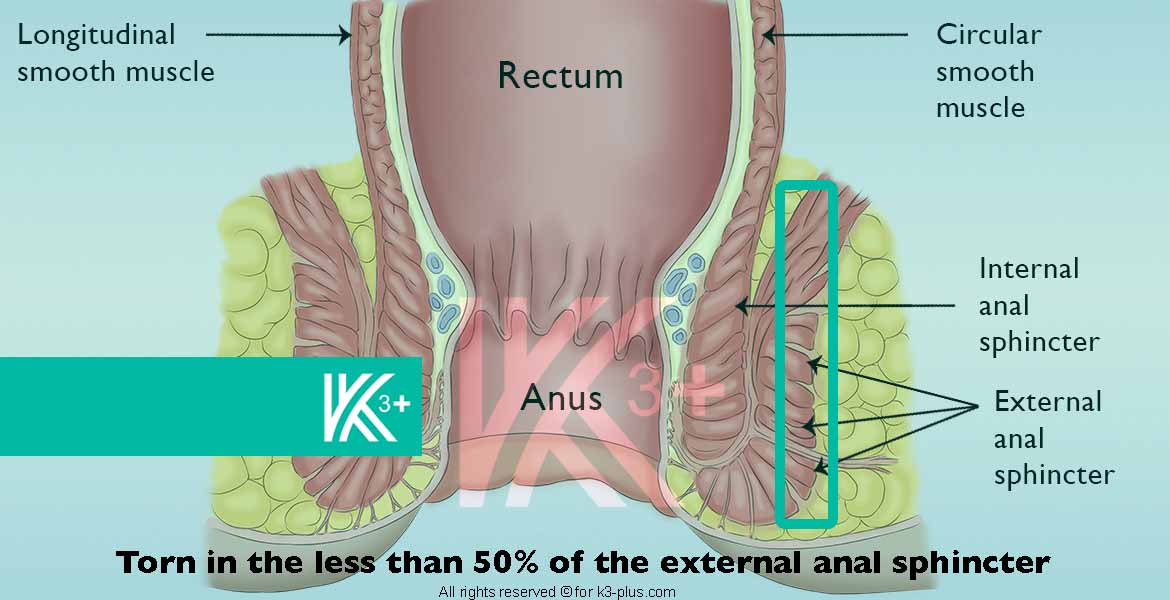
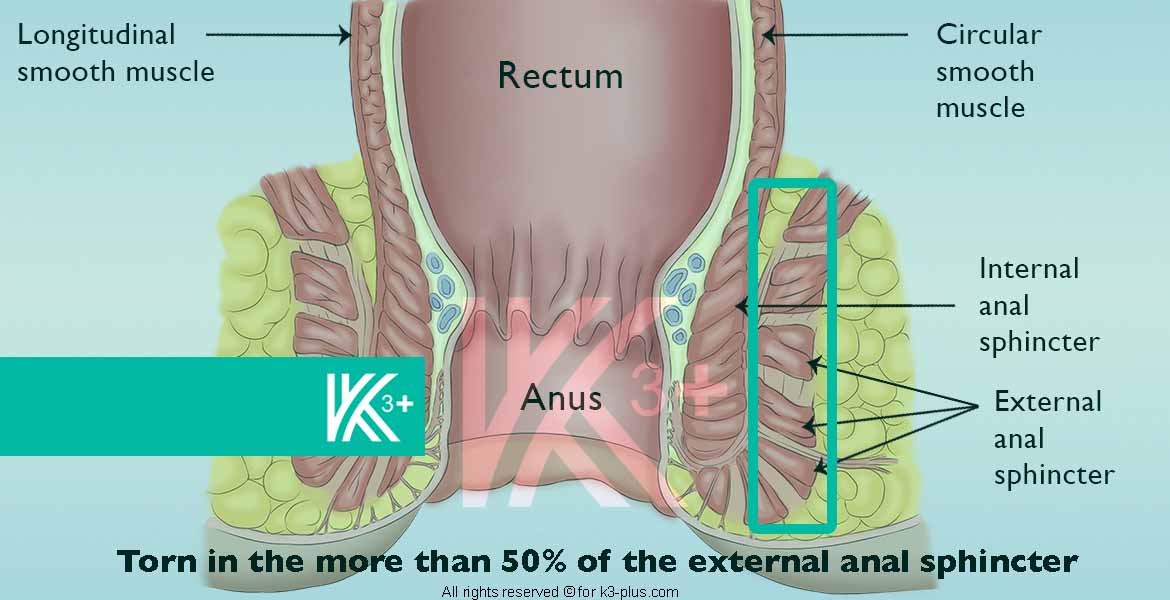
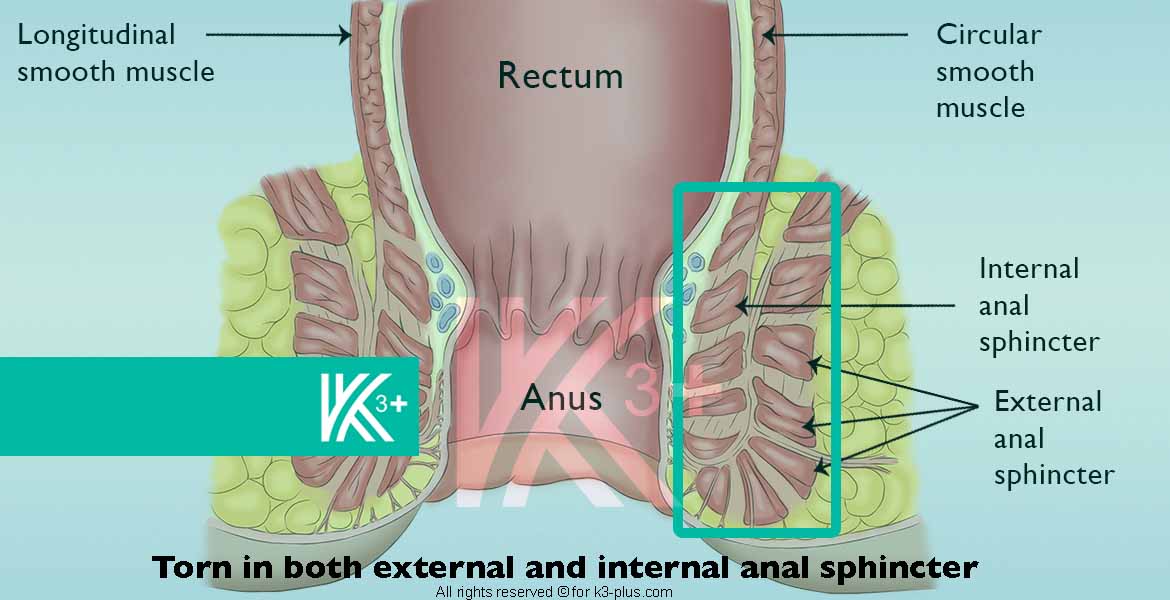
- Damage to the anal sphincter muscle
Any damage to the anal sphincter at the end of the rectum will make stool difficult to hold. This occurs during childbirth, for example, if it is difficult, and the use of episiotomy or forceps to assist in childbirth. - Nerve damage
There are nerves that sense incoming stool in the rectum and nerves that control contractions of the anal sphincter. Any damage to these nerves will lead to fecal incontinence. This nerve damage may occur due to:- Constant straining during bowel movements or due to a stroke or spinal cord injury.
- Some diseases such as diabetes and multiple sclerosis, they also affect these nerves and cause damage that results in fecal incontinence.
- Chronic constipation may be a hard, dry stool called stool that has been lodged in the rectum, and is too large to defecate and is larger than the anus. Muscles in the rectum and intestine stretch, causing them to eventually weaken. This allows watery stools deeper in the digestive system to move around the hard stool and leak out. Chronic constipation can also cause nerve damage and fecal incontinence.
- diarrhea.
Solid stool in the rectum can be easier to retain than liquid stool, so diarrhea may cause or even increase fecal incontinence. - Hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids may prevent the anus from closing completely when the veins in the rectum swell and allow stool in the rectum to leak out. - Rectal defect.
The rectum expands when needed to accommodate stool. But a fractured or hardened rectum cannot stretch enough and excess stool leaks out. - Surgery.
For example, surgery to treat hemorrhoids to treat enlarged veins of the rectum, and more complex surgeries in the anus, may damage muscles and nerves, causing fecal incontinence. - Rectal prolapse.
If the rectum descends into the anus, fecal incontinence occurs. - Rectocele in women,
in the solution of rectal defecation from the vagina, faecal incontinence can occur.
Factors that increase the risk of infection
- Age.
People over the age of 65 are at greater risk of fecal incontinence than others. - Gender
obstetric complications lead to fecal incontinence more - Hormone replacement therapy after menopause. Taking these hormones makes women vulnerable to faecal incontinence.
- Diseases
- With long-term diabetes or multiple sclerosis,
- these diseases may damage the nerves. The nerves that help in controlling defecation may be damaged and thus fecal incontinence may occur.
- Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
People with these diseases develop fecal incontinence in the advanced stages of their disease - Physical disability.
The rectal nerves may be damaged due to lack of access to the bathroom when you need to defecate directly, and this causes fecal incontinence.
Faecal incontinence degrees
Complications of faecal incontinence
- Shyness, frustration, and depression; Losing control over defecation can lead to isolationism, frustration, and social distancing.
- Irritation of the skin around the anus, as the skin in the anal area is very thin and has high sensitivity. Continuous contact with stool causes pain, itching and ulcers that need medical treatment.
Prevention of faecal incontinence
- Prevention of constipation. It is done by drinking more fluids and eating more food
- Prevention of diarrhea. Treating the causes of diarrhea, such as treating any inflammation in the intestine.
- Do not stress or reduce it as much as possible.
Fecal incontinence treatment
Artificial implants are a non-surgical treatment
They are self-expanding artificial implants equipped with the so-called shape memory that makes them grow by absorbing body fluids, reaching a volume of 730% of their original volume within 48 hours only, the surgical device used to place them is called the delivery system and has ten dispensers. Each dispenser has a cannula for inserting the artificial implants in place in the internal and external anal sphincter spaces where they are inserted through a specific delivery system. Some rare cases were resolved by the so-called implant departure easily and did not affect the efficacy.
Advantages of artificial implants in the treatment of fecal incontinence
- Biocompatible
- It does not cause allergic reactions
- Not carcinogenic
- Not degradable
- Not febrile
- Non-immune
- Biologically inert
- Complications in the short and long term
Real image during treatement
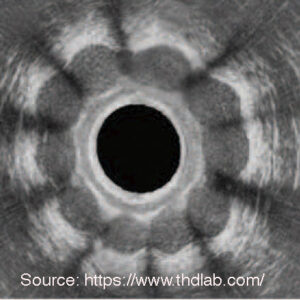


Real image using SphinKeeper for Faecal Incontinence treatment Source: https://www.thdlab.com
The device SphinKeeper



The device SphinKeeper used to treat Faecal Incontinence, Source: https://www.thdlab.com
Surgical treatment for faecal incontinence
Surgery may be necessary if there is another problem such as rectal prolapse or damage to the sphincter muscle due to childbirth. There are a number of surgical options:
Sphincteroplasty (repair of the anus)
The goal is to strengthen the muscles in the anal area and tighten the sphincter muscle. This is done by identifying the damaged muscles and releasing their edges, then gathering the edges of these muscles by sewing them together in an overlapping manner, which repairs the damaged or weak anal sphincter as a result of childbirth.
Sphincter repair
A process called “dynamic insole placement”. A muscle is taken from the inner thigh and used in the anal area by wrapping it around the sphincter muscle, and the tension of the body muscles is returned to the sphincter.
Treatment of rectal prolapse, rectocele, or hemorrhoids.
Treating associated conditions, if present, such as hemorrhoids, rectal prolapse, or rectocele reduces or completely treats fecal incontinence.
The artificial sphincter muscle
The anal sphincter is replaced by an artificial sphincter. An artificial sphincter is implanted around the anal canal. It is a small piece that can be blown into. When inflated, it tightly closes the anal sphincter and stool does not pass. When you need to defecate, air is deflated, the anus is opened, and stool is passed out. Then, when finished, the device inflates itself through a small external pump.
Colostomy
With it, the intestine is diverted to expel the stool from an opening in the abdomen instead of the anus, where the stool comes out into a special hanging bag. It represents the last resort if all other solutions fail.
Faecal incontinence FAQ
I have been suffering since my childhood, not being able to control the passage of gas, is this possible?
After the birth of my fourth child, I ran to the bathroom to catch myself before defecating. Is treating this complicated and needs surgery?
My son has autism and he also cannot control gases and stools sometimes, is this condition possible to solve?
I have a problem controlling defecation, but I have resolved that myself by eating food that causes me to have a type of constipation, such as yogurt and other things. Can that harm me?
What are Faecal Incontinence Possible Causes?
What are Faecal Incontinence Risk Factors?
What are Faecal Incontinence Signs & Symptoms?
What are Faecal Incontinence Diagnosis?
What are Faecal Incontinence Treatment Options?
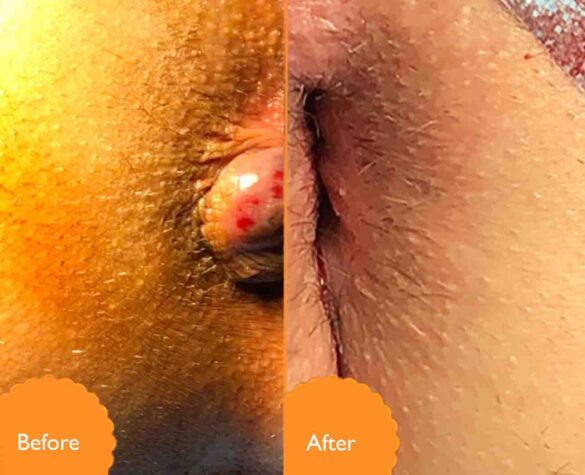
Faecal Incontinence Cases
Patients who previously lived suffering from hemorrhoids, fistulas, and hair bags, and received treatment by Dr. Khaldoun. We list the symptoms they suffered and the treatment that was provided, which could be useful for you.